Patient Education
Foot and Ankle Care of South Jersey provides patient education on common conditions we treat.
Please click on the condition to learn more.
If you are suffering from any of the conditions listed below,
please call us today, email: jrosenman@sjfoot.com or
click here to schedule an appointment with our specialist.
Common Conditions We Treat

Orthotics
Orthotics are prescription medical devices that you wear inside your shoes to correct biomechanical foot issues such as problems with how you walk, stand, or run. They can also help with foot pain caused by medical conditions such as diabetes, plantar fasciitis, bursitis, and arthritis. Orthotics might even help you avoid surgery to fix flat feet.
Foot Pain
Many foot and ankle problems develop as a result of injuries, congenital defects, degenerative diseases, impact, stress, and ill-fitting footwear; they can occur while walking, standing, working, running, and playing sports.It is important to have all foot and ankle injuries properly diagnosed and treated by a podiatrist as soon as discomfort or a change in the foot or ankle is detected in order to reduce pain and the chances of developing permanent damage and future health problems. Issues with the feet and ankles can be symptoms of a serious underlying health problem, such as cardiovascular disease and diabetes.
Heel Pain
Those that have heel pain on the bottom of their heel commonly have a condition called plantar fasciitis. The plantar fascia is a fibrous tissue that extends from the bottom of your heel to the bottom of your forefoot. This fascia can be inflamed from repetitive trauma such as running long distances, being on your feet all day, or from unsupportive shoes gear causing the foot to over-pronate or flatten out and stressing the plantar fascia. Sometimes you may even see bone spurs on the heel bone on an x-ray. The pain isn’t usually from the bone spur in most cases but from the micro tears caused by the stretching of the plantar fascia. If you wake up and the first step down on the ground hurts the worst, you most likely have plantar fasciitis.
Heel Spur
A heel spur is a calcium deposit causing a bony protrusion on the underside of the heel bone. On an X-ray, a heel spur can extend forward by as much as a half-inch. Without visible X-ray evidence, the condition is sometimes known as “heel spur syndrome.”
Treatments for heel spurs and associated conditions include exercise, custom-made orthotics, anti-inflammatory medications, and cortisone injections. If conservative treatments fail, surgery may be necessary.

Plantar Fasciitis
Plantar fasciitis is one of the most common causes of heel pain. It involves inflammation of a thick band of tissue that runs across the bottom of your foot and connects your heel bone to your toes (plantar fascia).
Plantar fasciitis commonly causes stabbing pain that usually occurs with your first steps in the morning. As you get up and move more, the pain normally decreases, but it might return after long periods of standing or after rising from sitting.
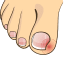
Ingrown Toe Nails
Ingrown toenails are a common condition in which the corner or side of a toenail grows into the soft flesh. The result is pain, redness, swelling and, sometimes, an infection. Ingrown toenails usually affect your big toe.
If the pain is severe or spreading, your doctor can take steps to relieve your discomfort and help you avoid complications of ingrown toenails.
Diabetic Neuropathy
Diabetic neuropathy is a type of nerve damage that can occur if you have diabetes. High blood sugar (glucose) can injure nerves throughout your body. Diabetic neuropathy most often damages nerves in your legs and feet.
Depending on the affected nerves, symptoms of diabetic neuropathy can range from pain and numbness in your legs and feet to problems with your digestive system, urinary tract, blood vessels and heart. Some people have mild symptoms. But for others, diabetic neuropathy can be quite painful and disabling.

Dry Skin
Dry skin isn’t usually serious, but it can be uncomfortable and unsightly.
Serious dry skin conditions — an inherited group of disorders called ichthyosis — can sometimes be disfiguring and upsetting. Fortunately, most dry skin is caused by environmental factors that can be at least partially controlled. These factors include hot or cold weather, low humidity, and soaking in hot water.
Warts
Common warts are small, grainy skin growths that occur most often on your fingers or hands. Rough to the touch, common warts also often feature a pattern of tiny black dots, which are small, clotted blood vessels.
Common warts are caused by a virus and are transmitted by touch. It can take a wart as long as two to six months to develop after your skin has been exposed to the virus. Common warts are usually harmless and eventually disappear on their own. But many people choose to remove them because they find them bothersome or embarrassing.

Hammertoes
Hammertoe is a foot deformity that occurs due to an imbalance in the muscles, tendons or ligaments that normally hold the toe straight. The type of shoes you wear, foot structure, trauma and certain disease processes can contribute to the development of these deformities.
A hammertoe has an abnormal bend in the middle joint of a toe. Hammertoe usually occurs in your second, third and fourth toes.
Relieving the pain and pressure of hammertoe may involve changing your footwear and wearing shoe inserts. If you have a more severe case of hammertoe, you might need surgery to get relief.
Callus
Calluses are thick, hardened layers of skin that develop when your skin tries to protect itself against friction and pressure. They most often develop on the feet and toes or hands and fingers. Calluses can be unsightly.
If you’re healthy, you need treatment for calluses only if they cause discomfort. For most people, simply eliminating the source of friction or pressure makes calluses disappear.
If you have diabetes or another condition that causes poor blood flow to your feet, you’re at greater risk of complications from calluses. Seek your doctor’s advice on proper care for calluses if you have such a condition.
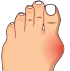
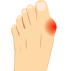
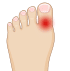
Bunions
A bunion is a bony bump that forms on the joint at the base of your big toe. It forms when your big toe pushes against your next toe, forcing the joint of your big toe to get bigger and stick out. The skin over the bunion might be red and sore.
Wearing tight, narrow shoes might cause bunions or make them worse. Bunions also can develop as a result of an inherited structural defect, stress on your foot or a medical condition, such as arthritis.

Flatfoot
You have flatfeet when the arches on the inside of your feet are flattened, allowing the entire soles of your feet to touch the floor when you stand up.
A common and usually painless condition, flatfeet can occur when the arches don’t develop during childhood. In other cases, flatfeet develop after an injury or from the simple wear-and-tear stresses of age.
Flatfeet can sometimes contribute to problems in your ankles and knees because the condition can alter the alignment of your legs. If you aren’t having pain, no treatment is usually necessary for flatfeet.
Gout
Gout is a common and complex form of arthritis that can affect anyone. It’s characterized by sudden, severe attacks of pain, swelling, redness and tenderness in the joints, often the joint at the base of the big toe.
An attack of gout can occur suddenly, often waking you up in the middle of the night with the sensation that your big toe is on fire. The affected joint is hot, swollen and so tender that even the weight of the sheet on it may seem intolerable.
Gout symptoms may come and go, but there are ways to manage symptoms and prevent flares.
Diabetic Foot Problems
Diabetic foot problems are a common and serious complication of diabetes. But you can often prevent diabetic foot problems or slow its progress with tight blood sugar control and a healthy lifestyle.
Call your doctor for an appointment if you have:
- A cut or sore on your foot that is infected or won’t heal
- Burning, tingling, weakness or pain in your hands or feet that interferes with daily activities or sleep
- Changes in digestion, urination or sexual function
- Dizziness

Peripheral Neuropathy
Peripheral neuropathy is the most common type of diabetic neuropathy. It affects the feet and legs first, followed by the hands and arms. Signs and symptoms of peripheral neuropathy are often worse at night, and may include:
- Numbness or reduced ability to feel pain or temperature changes
- Tingling or burning sensation
- Sharp pains or cramps
- Increased sensitivity to touch — for some people, even the weight of a bedsheet can be painful
- Muscle weakness
- Loss of reflexes, especially in the ankle
- Loss of balance and coordination
- Serious foot problems, such as ulcers, infections, and bone and joint pain
Painful High Arch
High arched feet, or a Cavus foot type, is simply an elevated longitudinal arch.The forefoot are declinated, or positioned downward, while the heel is anatomically inclinated, or positioned upward.Pain associated with high arched feet is very common, as the heels and forefeet are under excessive weight and pressure.Cavus foot can lead to a variety of painful symptoms and instability of both the foot and ankle.It’s important to have an accurate diagnosis, as it directly relates to treatment and future course.Majority of cases, symptomatic cavus foot types are treated conservatively with very positive results.

Ankle Sprain
A sprained ankle is an injury that occurs when you roll, twist or turn your ankle in an awkward way. This can stretch or tear the tough bands of tissue (ligaments) that help hold your ankle bones together.
Ligaments help stabilize joints, preventing excessive movement. A sprained ankle occurs when the ligaments are forced beyond their normal range of motion. Most sprained ankles involve injuries to the ligaments on the outer side of the ankle.
Treatment for a sprained ankle depends on the severity of the injury. Although self-care measures and over-the-counter pain medications may be all you need, a medical evaluation might be necessary to reveal how badly you’ve sprained your ankle and to determine the appropriate treatment.
Broken Toe
A broken toe is a common injury that’s most frequently caused by dropping something on your foot or stubbing your toe.
Usually, you can treat a broken toe by taping it to a neighboring toe. But if the fracture is severe — particularly if it involves your big toe — you may need a cast or even surgery to ensure proper healing.
Most broken toes heal well, usually within four to six weeks. Sometimes, a broken toe may become infected or increase the risk of osteoarthritis in that toe in the future.
Consult a doctor if the pain, swelling and discoloration continue for more than a few days or if the injury interferes with walking or wearing shoes.

Arthritis
Arthritis is inflammation of one or more of your joints. The main symptoms of arthritis are joint pain and stiffness, which typically worsen with age. The most common types of arthritis are osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis.
Neuroma
Neuroma is a painful condition that affects the ball of your foot, most commonly the area between your third and fourth toes. Neuroma may feel as if you are standing on a pebble in your shoe or on a fold in your sock.
Neuroma involves a thickening of the tissue around one of the nerves leading to your toes. This can cause a sharp, burning pain in the ball of your foot. Your toes also may sting, burn or feel numb.

Pediatric Foot Problems
Proper foot care is important for children of all ages. Various foot conditions that present into adulthood often stem from childhood problems… many can be avoided or lessened with proper diagnosis and treatment. Proper foot care for children is generally the same as adults, however we must keep in mind: children’s are still growing and their bones are softer; activity level of children is often higher than that of adults- ie sports and other activities; it is important to make sure shoe sizes are checked frequently, as there are growth spurts in addition to general growth. Foot and Ankle Care of South Jersey treats many pediatric problems. Dr. Rosenman treats both conservatively and surgically for children of all ages. Some treatments include casting infants suffering from severe in-toeing (ie- Clubfoot or Metatarsus Adductus), surgically separating webbed digits, bracing/splint for gait abnormalities and simple orthotic treatments for children suffering from Severs “syndrome.”

Stress Fracture
Stress fractures are tiny cracks in a bone. They’re caused by repetitive force, often from overuse — such as repeatedly jumping up and down or running long distances. Stress fractures can also arise from normal use of a bone that’s weakened by a condition such as osteoporosis.
Stress fractures are most common in the weight-bearing bones of the lower leg and foot. Track and field athletes and military recruits who carry heavy packs over long distances are particularly susceptible, but anyone can have a stress fracture. If you start a new exercise program, for example, you might develop stress fractures if you do too much too soon
Shin splints
If you have shin splints, you might notice tenderness, soreness or pain along the inner side of your shinbone and mild swelling in your lower leg. At first, the pain might stop when you stop exercising. Eventually, however, the pain can be continuous and might progress to a stress reaction or stress fracture.
Ankle Pain
Your ankle is an intricate network of bones, ligaments, tendons and muscles. Strong enough to bear your body weight and enable you to move, your ankle can be prone to injury and pain.
You might feel the pain on the inside or outside of your ankle or along the Achilles tendon, which connects the muscles in your lower leg to your heel bone. Although mild ankle pain often responds well to home treatments, it can take time to resolve. You should see your doctor for severe ankle pain, especially if it follows an injury.

Fungal Toe Nails
Nail fungus is a common condition that begins as a white or yellow spot under the tip of your fingernail or toenail. As the fungal infection goes deeper, nail fungus may cause your nail to discolor, thicken and crumble at the edge. It can affect several nails.
If your condition is mild and not bothering you, you may not need treatment. If your nail fungus is painful and has caused thickened nails, self-care steps and medications may help. But even if treatment is successful, nail fungus often comes back.
